With its ability to close regional gaps and improve patient access to medical services, telehealth care for the United States has become a revolutionary force in healthcare delivery. Through an examination of the subtleties, advantages, and difficulties of telehealth, this thorough manual clarifies how it affects American healthcare.
With its easy and effective remote healthcare service access, Telehealth Care For The United States has been rather popular in recent years. As healthcare paradigms change and technology improves, telehealth has become an essential part of the contemporary healthcare system. Explored in detail in this article are the development, advantages, difficulties, and prospects for telehealth.
Telehealth Care has been implemented in the US more and more in recent years, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic. Let us explore some of the most significant facets of telehealth application:
- Telehealth Trends:
- With the start of the COVID-19 epidemic, telehealth use grew quickly and still offers vital access to medical care.
- By March 2022, updated statistics indicate that telehealth will be used steadily, with a little larger percentage of video-based services than audio-only services.
- Disparities still exist among populations and within insurance kinds, nevertheless.
- Usage Rates:
- Over the course of the trial (April 14, 2021 through August 8, 2022), telehealth utilization rates ranged from 20.5% to 24.2%.
- Of adults, 22.0% said they had used telehealth within the previous four weeks on average.
- The lowest percentages of telehealth users were seen in the Midwest (18.7%), young persons (18–24) and uninsured (9.4%).
- Top rates were for those receiving Medicaid and Medicare (26.8% and 26.3%, respectively), Black people (26.1%), and those making less than $25,000 (26.4%).
- Access to video telehealth services is uneven, especially for certain racial and ethnic groups.
- Why Use Telehealth?:
- Telehealth allows you to:
- Speak with your doctor over the phone or via video.
- Safely send text messages to your medical professional.
- Utilizing technology, monitor your health and supply your doctor with details like your blood pressure.
- Telehealth allows you to:
- Equitable Access:
- Though telemedicine has grown, fair access to synchronous, real-time video telehealth is still a problem.
- A part of enhancing access to video telehealth services is played by factors including patient choices, broadband plans, technological resources, and literacy training programs.
Visit Telehealth.HHS.gov for additional information, which also offers best practices for delivering treatment via telehealth and keeps you informed about changes to billing and regulations.
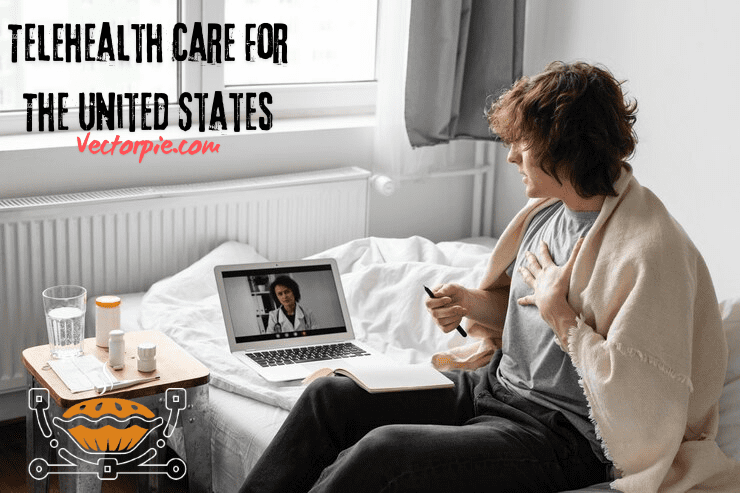
Defining Telehealth Care For The United States
Telehealth is the broad category of healthcare services provided remotely using telecommunications technologies. Through digital platforms, telehealth connects patients with healthcare professionals for everything from virtual consultations to remote monitoring, therefore removing traditional access obstacles.
Evolution of Telehealth Care
Early in the 20th century, radio transmission and telephony made it possible to have medical consultations from a distance. Real-time video consultations, remote monitoring equipment, and telemedicine apps have all been made possible by the revolutionization of telehealth throughout the years by developments in information technology and telecommunications.
Types of Telehealth Services
Asynchronous telehealth (store-and-forward technology), mobile health apps, remote patient monitoring, and synchronous telehealth are just a few of the modalities that make up telehealth services. These many platforms meet various healthcare demands and give patients and providers with convenience and flexibility.
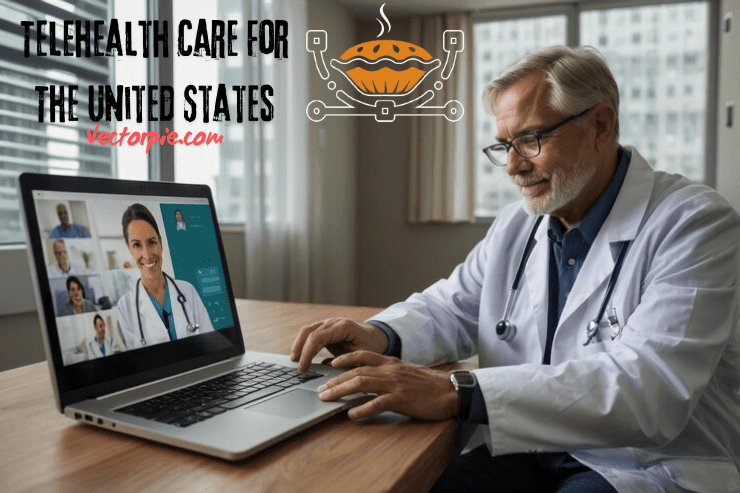
What are the benefits of telehealth?
Patients and providers can gain much from telehealth care, which has various advantages:
Convenience and Accessibility:
Remote Consultations: With telehealth care, patients can have in-home consultations with medical professionals. Patients who have mobility problems, those who live in rural or underdeveloped areas, and those who find it difficult to go to a physical clinic would benefit particularly from this.
Reduced Travel Time and Costs: By forgoing a trip to a clinic or hospital, patients save both time and money. Parking, waiting rooms, and commutes are all eliminated with telehealth.
Improved Access to Specialists:
By bridging geographic divides, telehealth care allows patients to see specialists who might not be available nearby. With telemedicine, a patient in a small town, for instance, can speak with a well-known cardiologist or neurologist.
Timely Care and Early Intervention:
Late-night consultations are made possible by telehealth care. Patients run less chance of problems by getting medical counsel right away.
Treating acute health problems, stopping the progression of diseases, and controlling chronic disorders all depend on early intervention.
Chronic Disease Management:
Patients with chronic illnesses (such diabetes, hypertension, or asthma) gain from routine telemedicine check-in visits. In addition to changing prescriptions and offering lifestyle advice, providers can track symptoms.
Proactive management encouraged by telehealth results in better health outcomes.
Mental Health Support:
One of the most significant aspects of mental health care is the utilization of telehealth care. Patients have the ability to make connections with therapists, counselors, and psychiatrists through the use of remote communication.
Through the utilization of confidential video conferences, patients are afforded the opportunity to discuss their emotional well-being, including matters pertaining to anxiety, depression, and stress.
After a first in-person appointment, telehealth is a great way to follow up. Patients may get medicine refills, talk about their progress, and voice concerns.
The ease with which this is possible improves treatment plan compliance.
Reduced Exposure to Infections:
When pandemics strike, such as COVID-19, telemedicine reduces exposure to infectious diseases. In busy waiting rooms, patients can get care without running the danger of contracting an infection.
Health Monitoring and Wearable Devices:
Wearable gadgets including blood pressure cuffs, glucose monitors, and fitness trackers are integrated with telehealth. Patients can provide providers their health information in real time.
Tracking development and spotting anomalies early on are made possible by remote monitoring.
Provider Collaboration and Second Opinions:
Professional cooperation in healthcare is made possible via telehealth. Specialists might confer with one another, go over test findings, and talk about course of therapy.
Patients don’t have to go great distances to get second views from professionals.
Health Equity and Inclusivity:
Reaching underprivileged groups like the elderly, the disabled, and those with little English language skills, telehealth advances health equity. Services for interpreting languages improve diversity.
Though telehealth has many advantages, when deciding between telehealth and in-person care, take into account your own needs, your privacy, and the nature of the medical problem.
How secure is telehealth Care?
Protecting patient privacy and data requires telehealth security. Telehealth platforms create safe communication channels by using encryption techniques, which protects data while it is in route. Role-based access control and user identification make that only authorized staff can see patient records.
It is required to have informed permission and privacy policies are transparent. HIPAA requirements for telehealth providers include safe transmission, storage, and access restrictions.
Infrastructure and platforms must be secure; manufacturers should provide advanced security features and cloud-based platforms should have robust security protocols. Smartphones, tablets, and PCs used by end users should all be safe, and telehealth software should only be downloaded from reliable websites. Both data retention and storage need to be encrypted and protected from hacking. Redundancy techniques and backup systems are crucial in times of emergency. Overall safety is promoted by patient education on telehealth security protocols.
What are the risks of telehealth security breaches?
Security lapses in telehealth seriously jeopardize patient privacy, data integrity, and system confidence. Key hazards include software flaws, patient identity theft, malware and ransomware attacks, insecure end-user devices, inadequate data storage security, lack of HIPAA compliance, and loss of trust and reputation damage.
Telehealth providers must give security measures first priority, carry out regular audits, inform consumers about safe practices, and interact with cybersecurity experts in order to lessen these risks. Through resolution of these issues, telehealth providers may guarantee the security and integrity of patient data, fostering trust and reducing the likelihood of telehealth business breaches.
How can I protect my telehealth sessions from breaches?
Guide to Telehealth Security Best Practices
• Select a Secure Platform: Make sure the telehealth platform you choose is respectable and gives security and HIPAA rules top priority. Give data transmission end-to-end encryption.
• User Authentication: For extra protection, use multi-factor authentication and robust, original passwords. In telehealth sessions, confirm the identity of medical professionals.
• Secure Devices: Maintain software and operating systems current and use secure devices. Steer clear of public or unprotected Wi-Fi networks.
• Virtual Waiting Rooms: Waiting in virtual waiting rooms will stop unwanted access to ongoing consultations.
• Session Controls: Providers need to have control over telehealth sessions and make sure that only approved participants are there.
• Privacy Settings: Learn about the privacy settings on the telehealth platform and exercise caution while sharing your screen during sessions.
• Secure Communication Channels: Stay away from sending private information over unprotected messaging apps or standard email by using the encrypted channels available within the telehealth platform.
• Patient Education: Encouraging patients to utilize secure equipment and report any unusual behavior, educate them about telehealth security procedures.
• Data Retention Policies: Verify adherence to privacy laws and learn how long the telehealth platform keeps patient data.
• Secure Setting: Keep other programs or windows closed during telehealth sessions and conduct them in a quiet, private setting.
• Frequent Security Audits: To spot vulnerabilities and quickly fix any flaws, do frequent security audits.
Challenges and Limitations Of Telehealth Care
Digital Divide
Widespread use of telehealth is severely hampered by the digital divide, as underprivileged groups find it more difficult to access the internet and use technology. It will take addressing these differences to guarantee that every American has fair access to telehealth services.
Regulatory and Reimbursement Barriers
States’ different telehealth laws make the regulatory environment for healthcare providers complicated. Reimbursement rules for telehealth services are also still problematic; their limits and inconsistencies prevent their broad use and sustainability.
Privacy and Security Concerns
Telehealth’s remote character begs questions about data security and patient privacy. Patient data protection and telehealth platform trust need strict adherence to HIPAA rules and the deployment of strong cybersecurity safeguards.
Quality of Care
Though telehealth has numerous advantages, questions about the effectiveness and quality of remote healthcare delivery still exist. High standards of treatment in telehealth environments depend on ensuring sufficient training for healthcare professionals, putting evidence-based practices into practice, and tracking quality indicators.
Future Outlook
Technological Advancements
The breadth and efficacy of telehealth services may be greatly expanded by technological developments in telehealth, such as virtual reality, remote monitoring devices, and artificial intelligence. These developments should increase patient outcomes, streamline healthcare delivery even further, and increase access to specialized treatment.
Policy and Regulatory Reforms
Expansion and sustainability of telehealth depend on removing regulatory obstacles and simplifying reimbursement procedures. To implement significant changes and guarantee fair access to telehealth services nationwide, legislators, healthcare stakeholders, and technology providers must work together.
Cultural Shift Towards Telehealth
The COVID-19 epidemic sped up the use of telemedicine and sparked a societal change in favor of providing healthcare remotely. Telehealth is set to become a common element of the healthcare ecosystem as patients grow used to virtual consultations and remote monitoring, spurring innovation and changing care delivery paradigms.
Telehealth Care For The United States: FAQs
What is Telehealth Care For The United States?
In the United States, telehealth care is the provision of healthcare services remotely via telecommunications technology, allowing patients to obtain treatment from any location with an internet connection.
How does Telehealth benefit patients?
Telehealth lowers healthcare costs, increases patient access to medical services, and gives patients more control over their care.
Are there any privacy concerns associated with Telehealth?
Indeed, the remote character of telehealth presents issues with patient data security and privacy. Tackling these issues requires putting strong cybersecurity protections in place and making sure HIPAA rules are followed.
What are the challenges of Telehealth adoption?
The digital gap, obstacles related to regulations and reimbursements, worries about security and privacy, and guaranteeing the standard of treatment in remote healthcare delivery are among the challenges.
What technological advancements are shaping the future of Telehealth?
Future telehealth service coverage and efficacy are expected to be improved by technological breakthroughs including virtual reality, remote monitoring devices, and artificial intelligence.
How can policymakers support Telehealth expansion?
By removing legal obstacles, simplifying reimbursement procedures, and encouraging fair access to telehealth services across the country, legislators can help telehealth grow.
Conclusion
For the United States, telehealth care is a paradigm change in healthcare delivery that gives hitherto unheard-of chances to improve patient involvement, efficiency, and access. Notwithstanding obstacles, telemedicine keeps developing and growing, spurring creativity and changing the healthcare industry. The United States may fully realize the potential of remote healthcare delivery and guarantee improved health outcomes for all by embracing telehealth technologies and removing adoption obstacles.
Must Read : USAA Pet Insurance : Secure Your Furry Friend’s Future
Also Read : Nationwide Insurance Company: Protecting Your Future
Must Read : 7 Best Virtual Credit Cards for Businesses in 2024
Read This : USAA Home Insurance : Your Guide For Best Home Insurance