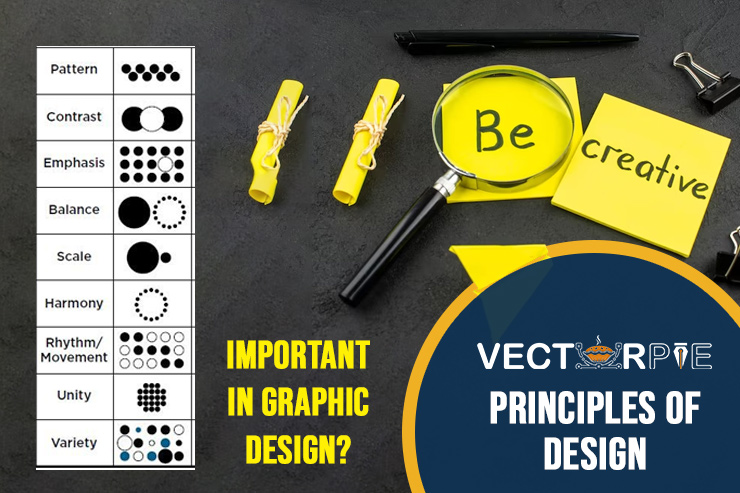
Design principles are fundamental guidelines that govern how elements are arranged in a composition. They serve as the building blocks of all visual arts, providing a framework for creating aesthetically pleasing and functional designs.
Why Are They Important in Graphic Design?
In graphic design, understanding and applying design principles can elevate a design from good to exceptional. They help designers make informed decisions about layout, color, typography, and other elements to achieve the desired impact.
Balance in Design
Asymmetrical Balance
Asymmetrical balance is achieved by placing different elements of varying visual weight on either side of the central axis. It adds dynamism and visual interest to a composition.
It is often used in circular or spherical designs to create a sense of movement and harmony.
Emphasis and Focal Points
Creating Visual Hierarchy
Visual hierarchy refers to the arrangement of elements to guide the viewer’s eye through the design. It helps establish the most important elements and their order of importance.
Using Contrast Effectively
Contrast involves using differences in color, size, shape, or texture to create emphasis and highlight key elements.
Alignment and Consistency
Importance of Grid Systems
Grid systems provide a framework for organizing content, ensuring alignment, and maintaining consistency across a design. They help create a structured and organized layout.
Ensuring Visual Cohesion
Visual cohesion is achieved by aligning elements along a common axis or using consistent spacing and proportions. It enhances readability and clarity in a design.
Repetition and Patterns
Establishing Visual Rhythm
Repetition of elements such as shapes, colors, or textures creates a sense of rhythm and unity in a design. It helps tie the composition together.
Using Patterns to Create Interest
Patterns add visual interest and texture to a design. They can be subtle background elements or bold focal points, depending on the desired effect.
Proportion and Scale
Playing with Size and Scale
Proportion refers to the relationship between elements, while scale refers to their size relative to the design as a whole. Manipulating these factors can create dramatic or harmonious effects.
Ensuring Harmonious Proportions
Harmonious proportions create a sense of balance and unity in a design. They guide the viewer’s eye smoothly across the composition.
Typography and Readability
Choosing the Right Fonts
Typography plays a crucial role in conveying tone and personality in a design. Choosing the right fonts ensures readability and enhances the overall aesthetic.
Understanding Text Hierarchy
Text hierarchy involves using different font sizes, weights, and styles to prioritize information. It helps readers navigate the content easily.
Color Theory in Design
Psychological Impact of Colors
Colors evoke emotions and convey messages in a design. Understanding color psychology helps designers create mood-appropriate compositions.
Creating Color Palettes
Color palettes define the overall look and feel of a design. They can be monochromatic, complementary, analogous, or triadic, depending on the desired effect.
White Space and Minimalism
The Power of Negative Space
White space, or negative space, refers to the empty areas in a design. It allows elements to breathe and enhances visual clarity.
Achieving Balance with Less
Minimalism emphasizes simplicity and clarity by using only essential elements. It removes clutter and distractions, focusing on the core message.
Unity and Harmony
Ensuring Elements Work Together
Unity in design is achieved when all elements come together cohesively to create a harmonious whole. It ensures a seamless and integrated composition.
Creating a Cohesive Design Language
A cohesive design language involves using consistent styles, colors, and elements throughout a project. It reinforces brand identity and recognition.
Movement and Flow
Guiding the Viewer’s Eye
Movement in design directs the viewer’s gaze through the composition, leading them from one element to another. It creates a narrative and visual interest.
Creating Dynamic Designs
Dynamic designs incorporate elements that imply motion or action. They engage the viewer and create a sense of energy within the composition.
Experimentation and Creativity
Breaking the Rules
While understanding design principles is important, creativity often thrives when rules are bent or broken. Experimentation leads to innovative and original designs.
Pushing Boundaries for Innovation
Designers who push boundaries and explore new techniques contribute to the evolution of the field. It inspires fresh perspectives and keeps design relevant.
Accessibility and Inclusivity
Designing for All Audiences
Accessible design ensures that everyone, regardless of ability, can interact with and understand a design. It considers factors such as readability, color contrast, and navigation.
Ensuring User-Friendly Experiences
Inclusive design goes beyond accessibility to create experiences that cater to diverse audiences. It embraces empathy and understanding of users’ needs.
Technology and Design Evolution
Impact of Technology on Design
Advancements in technology continually reshape the landscape of graphic design. From digital tools to interactive experiences, technology opens new possibilities.
Embracing Change for Progress
Designers who embrace technological advancements stay ahead of the curve. It allows for the exploration of new mediums and techniques for impactful design.
F&Q’s
1. What are the most important design principles for beginners?
Beginners should focus on understanding balance, emphasis, alignment, and typography as foundational design principles.
2. How does color psychology influence design choices?
Color psychology helps designers evoke specific emotions or convey particular messages through color choices in their designs.
3. Why is white space important in graphic design?
White space allows for visual clarity, helps in organizing elements, and enhances readability in a design.
4. How can I create a cohesive color palette for my design project?
Start by selecting a base color and then choose complementary or analogous colors to create a harmonious palette.
5. What role does user experience (UX) design play in graphic design?
UX design focuses on creating intuitive and user-friendly experiences in graphic design, ensuring that designs are not only visually appealing but also easy to navigate and understand.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the principles of design form the backbone of every successful graphic design project. By understanding and applying these principles, designers can create visually appealing, functional, and impactful designs that resonate with their audiences. Whether it’s balancing elements, creating focal points, or experimenting with typography and color, each principle plays a crucial role in the creative process.
Now, armed with this guide, go forth and unleash your creativity. Remember to keep learning, exploring, and pushing the boundaries of design innovation.

1 thought on “The Principles of Design: A Guide for Graphic Designers”